Difference between revisions of "Fortran1"
GregTourte (talk | contribs) m |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
The examples are available via svn: | The examples are available via svn: | ||
| − | < | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="shell"> |
svn co https://svn.ggy.bris.ac.uk/subversion-open/fortran1/trunk fortran1 | svn co https://svn.ggy.bris.ac.uk/subversion-open/fortran1/trunk fortran1 | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
=hello, world= | =hello, world= | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
and run it by typing: | and run it by typing: | ||
| − | < | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="shell"> |
./hello_world.exe | ./hello_world.exe | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
Examine the contents of hello_world.f90, using '''cat''', '''less''', '''more''' or your favourite text editor, and you'll see: | Examine the contents of hello_world.f90, using '''cat''', '''less''', '''more''' or your favourite text editor, and you'll see: | ||
| − | < | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="fortran"> |
! | ! | ||
! This is a comment line. | ! This is a comment line. | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
write(*,*) "hello, world" | write(*,*) "hello, world" | ||
end program hello_world | end program hello_world | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
We have: | We have: | ||
Revision as of 13:03, 22 November 2022
Fortran1: The Basics
Getting the content for the practical
We'll use GCC and Intel Fortran compilers. You need to load these modules on BlueCrystal phase 3:
module add tools/subversion-1.8.4 languages/intel-compiler-16-u2 languages/gcc-7.1.0
The examples are available via svn:
svn co https://svn.ggy.bris.ac.uk/subversion-open/fortran1/trunk fortran1
hello, world
This program prints "hello, world" to the screen.
cd fortran1/examples/example1You can compile the program by typing:
gfortran hello_world.f90 -o hello_world.exeor by typing:
makeand run it by typing:
./hello_world.exe
Examine the contents of hello_world.f90, using cat, less, more or your favourite text editor, and you'll see:
!
! This is a comment line.
! Below is a simple 'hello, world' program written in Fortran90.
! It illustrates creating a main 'program' unit together
! with good habits, such as using 'implicit none' and comments.
!
program hello_world
implicit none
write(*,*) "hello, world"
end program hello_world
We have:
- Comments, which start with an exclamation mark !. These can start anywhere on the line.
- The start of the program is given by the optional statement program followed by the optional program name.
- The implicit none statement forces explicit declaration of all data objects - variables, types, interfaces, etc. More of that in the next section. Use it always!
- A write statement, printing the given string to the screen (first asterisk *) with default formatting (second asterisk *).
- The end of the main program is given by the mandatory statement end, followed by the optional program name.
Open up your text editor and try changing the greeting, just for the heck of it. Retype make and re-run it. We'll adopt a similar strategy for all the other examples we'll meet. If you ever want to get back to the original version of a program, just type:
svn revert hello_world.f90Although this has all been fairly painless, we have made a very significant step - we are now editing, compiling and running Fortran programs.
Now try to use the Intel compiler instead of gfortran:
make clean
make FC=ifortor directly:
ifort hello_world.f90 -o hello_world.exeRun it and make sure the output is the same.
Containers and the Types of Things
As fun as "hello, world" was, let's spice things up a little. For instance, let's introduce some variables. We'll need to move to the next example:
cd ../example2Fortran has several intrinsic, or built-in, types. Every variable must be given a type. Take a look in basic_types.f90:
character :: sex ! a letter e.g. 'm' or 'f'
character(len=12) :: name ! a string
logical :: wed ! married?
integer :: numBooks ! must be a whole number
real :: height ! e.g. 1.83 m (good include units in comment)
complex :: z ! real and imaginary parts
This set of types suffice for a great many programs. The above are all single entities. We'll meet arrays of things in a couple of examples time. In Fortran2, we'll also meet user-defined types. These allow us to group instances of intrinsic types together forming new kinds of thing--new types. User-defined types are the bees knees and can make programs much easier to work with. We'll leave the details to that later course, however.
The above snippet shows some variable declarations, along with a helpful comments. It's good practice to comment your declarations, as a programmer new to your code (or even yourself in a couple of months time) can have a hard time figuring out what is supposed to be stored in such-and-such a variable. While we're on the topic, it's also good practice to give your variables meaningful names, even if they are long. Trust me, a bit more typing now, perhaps, but a lot less head-scratching later on over what is stored in the inspiringly named xbNew, or z2!
It's often a good idea to give variables an initial value when we declare them (working with uninitialised variables in another common source of bugs). This time we're looking at more_types.f90:
character :: nucleotide = 'A' ! DNA has A,C,G & T
character(len=50) :: infile = 'yourData.nc', outfile = "myData.nc"
logical :: initialised = .true. ! or .false.
real :: solConst = 1.37 ! Solar 'constant' in kW/m^2
complex :: sqrtMinusOne = (0.0,1.0) ! (real,imag)
Fortran also allows us to gives variables certain attributes. For example, from pitfalls.f90:
real, parameter :: pi = 3.14159 ! a fixed constant
The parameter attribute tells you, me and Fortran that pi is a constant. It's fixed and it's a compile-time error if we try to change it. This is a good thing, since we can catch nasty bugs that can creep in that way. We never want pi to be anything other than pi, right?! Assigning parameter attributes to quantities we know are constant is an example of defensive programming, or bug avoidance!
All intrinsic, i.e. built-in Fortran data types are available in several kinds. For integers the kind implies the maximum number of digits. For real and complex varaibles and parameters the kind implies the precision and the exponent range. There are several ways to set kinds. The most portable way is use the intrinsic functions:
selected_int_kind( r )
selected_real_kind( [p] [,r] )
where the arguments in square brackets [...] are optional.
If I need an integer variable to store up to 8 digits of information, I can define it like this:
integer, parameter :: int_kind = selected_int_kind( 8 )
integer( kind=int_kind ) :: i
If I need a real or a complex variable to represent a floating point number with 16 digits after the decimal point and with the decimal exponent range of at least 100, I can define it like this:
integer, parameter :: r_kind = selected_real_kind( 16, 100 )
real( kind=r_kind ) :: r
complex( kind=r_kind ) :: c
The third program illustrates some arithmetic pitfalls--beware!:
- integer division and it's truncation
- casting as a solution to mismatched types
- (integer) overflow
- (real number) underflow
Let's have a play with the programs. You an compile them by typing:
makeand run them by typing, e.g.:
./basic_types.exeor,
./more_types.exeor,
./pitfalls.exeAlthough we compiled our first example by-hand, we'll be using make to compile the rest of our example programs, so you won't have to worry about that side of things. (If you'd like to know more about make, you can take a look at our course on make, presented in a very similar style to this here excursion into Fortran.)
Now modify the program (remembering svn revert intrinsic_types.f90 if you make a mess). Try giving values to various types and also using operators such as:
- arithmetic: +, -, /, ** (exponentiation)
- functions: sin, cos, floor (rounding down)
- logic: .and., .or., .not., .eqv., .neqv.
- and you'll meet many more in the future..
For example:
- Calculate the surface area of a sphere.
- Is sine of pi divided by four really the same as one over root two?
- What is the truth table of the NAND operator?
If, Do, Select and Other Ways to Control the Flow
Programs are like cooking recipes. We've covered the how much of this and how much of that part. However, we also need to cover the doing bit--do this and then do that, and for how long etc. This is generically termed control flow. Fortran gives us a fairly rich language with which to describe how we would like things done. Next example:
cd ../example3
Take a look inside control.f90. We have some variable declarations and then we encounter our first conditional:
if (initialised .eqv. .true.) then
write (*,*) "The variable 'area' is initialised and has the value:", area
else
write (*,*) "The variable 'area' is NOT initialised and has the value:", area
end if
This is fairly self eplanatory--if..something is the case..then..else.. You can also have an elseif. In fact you can have as many of those as you like. You can also have as many statements inside each clause as you like. Talk about spoiled!
Select is another control structure:
select case (nucleotide)
case ('A')
write (*,*) "nucleotide is Adenine"
case ('G')
write (*,*) "nucleotide is Guanine"
case ('T')
write (*,*) "nucleotide is Thymine"
case ('C')
write (*,*) "nucleotide is Cytosine"
case default
write (*,*) "default is the catch-all. 'Fall-through' can be a nasty bug."
stop
end select
This is a neat way of saying, "if..then..elsif..else.." The default clause at the bottom is important. Dropping this off can lead to fall-through, where none of the cases triggered. This is rarely what you want and can lead to nasty bugs.
Our first do loop is of the form:
do ii=1,5
write (*,*) "Do loop counter ii is:", ii
end do
Again, this is fairly readable. ii is first given the value of 1, the body of the loop is evaluated and then we go back to the top again. Except this time we increment the counter (ii) by the default amount, which is 1. When we're at the top and we take ii past 5, we stop the loop and move on to the next statement passed the end do. You're allowed as many statements inside the loop as you like. Indeed, you're allowed more loops, conditions, loops in loops, just about anything you can think of! Beware, however, debugging a huge construct of nested this that and the other can be beyond the limits of human patience. Keep our programs simple and you will be happier for it.
The other loop examples show variations in the stopping condition and stride (i.e. how much we increment by), including counting backwards, and stopping before we've even started!
You'll notice that all the loops we've seen thus far will run for a pre-determined number of iterations. What if we don't know how many iterations we want ahead of time. Some languages, such as C for example, include a while loop for this purpose. In Fortran we still use do, but omit any start and end conditions. Note that we must include an exit condition, if we want such a loop to terminate:
threshold = 0.5
ii = 0
do
call random_number( random_value )
if (random_value .gt. threshold) then
print*, 'counter is:', ii, random_value, '>', threshold, 'stopping.'
exit
end if
print*, 'counter is:', ii, random_value, '<', threshold
ii = ii+1
end do
As before, compile it, run it and generally muck about. These are only a few of the control structures provided to us by Fortran. You'll find that you can do most things with these three, however.
Before leaving this example, let's consider if tests containing an equals and floating point numbers. Remember that there are an infinite set of real numbers and so a computer can only approximate them. For example, how would a computer represent 10/3? It has limited precision. It follows therefore that we should be careful when we need to test whether a real number is equal some value, such as 3.3 (see the last section of the program). A common way around this problem is to subtract the first real from second and to compare the absolute value of the result to some small threshold (to account for rounding errors).
if ((abs(val-ref)) .lt. 0.0001) then
...
end if
Exercises
- Write a select statement which prints out the names of the digits in the set [1,10] in different languages. Write a loop to trigger each of these print statements.
- Write a nested loop: Write a pair of nested do loops which count between 1 and 3. Print the values of the two counters in the inner-most loop. Think about where your 'end do's should go.
- Write a nested if statement: For example, create character variables called 'vehicle', 'colour' and 'size'. We could represent a small red car as; vehicle = 'c', colour = 'r' and size = 's'. Arrange for your nested if to print 'eureka' given a big green train. Think about where your 'end if' statements should go.
Not one, Many!
That was fun. Back to thinking about variables for a moment:
cd ../example4
Last time we declared just one thing of a given type. Sometimes we're greedy! Sometimes we want more! To be fair, some things are naturally represented by a vector or a matrix. Think of values on a grid, solutions to linear systems, points in space, transformations such as scaling or rotation of vectors. For these sorts of things the kings and queens of Fortran gave us programmers arrays. Take a look inside static_array.f90:
real, dimension(4) :: tinyGrid = (/1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0/)
real, dimension(2,2) :: square = 0.0 ! 2 rows, 2 columns, init to all zeros
real, dimension(3,2) :: rectangle ! 3 rows, 2 columns, uninit
The syntax here reads, "we'll have an one-dimensional array (i.e. vector) of 4 reals called tinyGrid, please, and we'll set the initial values of the cells in that array to be 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 and 4.0, respectively.
For the second and third declarations, we're asking for two-dimensional arrays. One with two rows and two colums, called square, and one with three rows and two colums. We're calling that rectangle.
The program then goes on to print out the contents of tinyGrid.
If we want to access a single element of an array, we can do so by specifying it's indices:
write (*,*) "square(1,2) is the top right corner:", square(1,2)
Fortran provides a couple of handy intrinsic routines for determining the size (how many cells in total) and the shape (number of dimensions and the extent of each dimension) of an array.
write (*,*) "size(rectangle) gives total number of elements:", size(rectangle)
write (*,*) "shape(rectangle) gives rank and extent:", shape(rectangle)
Fortran also allows us to reshape an array on-the-fly. Using this intrinsic, we can copy the values from tinyGrid into square. Neat.
square = reshape(tinyGrid,(/2,2/))
Fortran also provides us with a rather rich set of operators (+, -, *, / etc.) for array-valued variables. Have a go at playing with these. If you know some linear algebra, you're going to have a great time with this example!
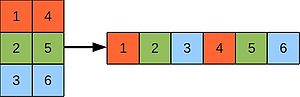
One thing to bear in mind when we consider 2D arrays is that Fortran stores them in memory as a 1D array and 'unwraps' them according to column-major order:
Exercises
- Create 3x3 grid to store the outcome of a game of noughts-and-crosses (tic-tac-toe), populate it and print the grid to screen.
- Fortran allows you to slice arrays. For example the second column of the 2d-array 'a' is a(:,2). Print the third row from the grid above.
- Add two vectors together. Is this algebraically correct? What about adding two matrices?
- Create two 2-d arrays. Populate one randomly and create another as a mask. Combine the two matrices and print the result.
The static malarky is because Fortran also allows us to say we want an array, but we don't know how big we want it to be yet. "We'll decide that at run-time", we programmers say. This can be handy if you're reading in some data, say a pay-roll, and you don't know how many employees you'll have from one year to the next. Fortran calls these allocatable arrays and we'll meet them in Fortran2.
If Things get Hectic, Outsource!
cd ../example5Now, as we get more ambitious, the size of our program grows. Before long, it can get unwieldy. Also we may find that we repeat ourselves. We do the same thing twice, three times. Heck, many times! Now is the time to start breaking your program into chunks, re-using some from time-to-time, making it more manageable. Fortran gives us two routes to chunk-ification, functions and subroutines.
Let's deal with subroutines first. In procedures.f90, scroll down a bit and you can see:
subroutine mirror(len,inArray,outArray)
implicit none
! dummy variables
integer, intent(in) :: len
character,dimension(len),intent(in) :: inArray
character,dimension(len),intent(out) :: outArray
! local variables
integer :: ii
integer :: lucky = 3 ! notice scope of this identically named variable
do ii=1,len
outArray(len+1-ii) = inArray(ii)
end do
write (*,*) "'lucky' _inside_ subroutine is:", lucky
end subroutine mirror
Now, note that this is outside of the main program unit. (In principle, we could hive this off into another source code file, but we'll leave that discussion until Fortran2.) Notice also that we have a shiney implicit none resplendent at the top of the subroutine. Overall, it looks pretty similar to how a main program unit might look, but with the addition of arguments. Those fellows in the parentheses after the subroutine name. The declaration part also lists those arguments and we've commented that this are so-called dummy variables. We also see an attribute that we've not seen before, called intent. This is a very handy tool for defensive programming (remember aka bug avoidance). Using intent we can say that the integer len is an input and as such we're not going to try to change it. Likewise for the charcter array inArray. It would be a compile-error if we did. We also state that the character array outArray is an output and we're going to give it a new value come what may! We also have some variables that are local. Interestingly enough, one of our local variables, the integer called lucky, has exactly the same name as a variable in the main program unit. When we run the program, however, we will see that the two do not interfere with each other. This is down to their scope. The scope of lucky in the main program is all and only the main program unit and the scope of lucky in the subroutine is all and only the subroutine. We say that the main program unit and the subroutine units have different name spaces.
Well, we've seen a lot of new syntax and concepts in all that. Useful ones though. This program is small and artificial, so it's hard to see the benefits just yet. You will, however, as your programs grow. The subroutine is called from the main program , funnily enough by a call statement. Notice how the arguments passed to the subroutine in the call statement also have different names in the main program and the subroutine. That's scope again.
Functions similar yet different to subroutines. Notice that we don't call them in the same way. We still pass arguments, but the functions returns and value, and so we could place a function on the right-hand side (RHS) of an assignment. Typically we would write a function for a smaller body of work. We can potentially invoke it in a neater way from our main program, however.
Looking at the body of the function:
function isPrime(num)
implicit none
! return and dummy variables
logical :: isPrime
integer, intent(in) :: num
select case (num)
case (2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29)
isPrime = .true.
case default
isPrime = .false.
end select
end function isPrime
we can see that we have a declaration for a variable with the same name as the function. The type of this variable is the return type of the function. Indeed the value of this variable when we reach the bottom of the function is the value passed by to the calling routine. Note that we can call functions and subroutines from other functions and subroutines etc. in a nested fashion.
The last thing of note is the funky interface structure at the top of the main program:
interface
function isPrime(num)
logical :: isPrime
integer, intent(in) :: num
end function isPrime
end interface
Our function definition is outside of the main program and so is said to be external. The main program unit needs to know about it, however, and an interface structure is a good way to do this as it prompts Fortran to check that all the arguments match up between the call and the definition. It's the way to do it..for now. (We'll meet Fortran modules in Fortran2, which will give us a neater way to perform the same checks.)
Try running the program and writing some functions and subroutines of your own.
Exercises
- Write a simple error handling subroutine that stops the program after printing a message, which is passed in as an argument.
- Does the surface area of a circle increase linearly with an increase in radius? How about circumference? Write some functions and a loop to investigate.
- What happens if you write a function which calls itself?
Input and output
OK, say we want some permenance? Perhaps we want to record the outputs of our program for some time, or we want to read the same values into a program each time that we run it. Storing data in files is the way to go.
File i/o
cd ../example6
In this example we'll see how to read and write data to and from files. The code for this example in contained in file_access.f90.
Before we can either read from- or write to- a file, we must first open it. Funnily enough, we can do this using the open statement, e.g.:
open(unit=19,file="output.txt",form='formatted',status='old',iostat=ios)
- unit is a positive integer given to the file so that we can refer to it later. Several numbers are reserved, however, so we must avoid 5 (keyboard), 6 (screen), 101 (stdout) & 102 (punch card!).
- file is a character string (can be 'literal') containing the name of the file to open.
- form is the file format--'formatted' (text file) or 'unformatted' (binary file).
- status specifies the behaviour if the file exists:
- old the file must exists
- new the file cannot exists prior to being opened
- replace the old file will be overwritten
- iostat is a non-zero integer in case of an error, e.g. the file cannot be opened for instance.
When you have finished with a file, you must close it:
close(19)
Note that if you need to go back to the beginning of a file, you don't have to close it and open it again, you can rewind it:
rewind(19)
To write to a file, the syntax is, e.g.:
write(unit=19,fmt=*) array1, array2
where,
- array1 & array2 are variables we wish to write to the file.
- unit is the unit number of the file we want write to.
- fmt is a format string. We have chosen '*', which gives us default settings. However, we can gain greater control by specifying in detail what we will be writing and how we would like it formatted. Take a look in the example file_access.f90 for examples.
Similarly, we use a read statement to extract data from a file, e.g.:
read(unit=19,fmt=*,iostat=ios) var1, var2
Note is that it is very important to use the iostat attribute to make sure that we handle any errors, and don't press on regardless into oblivion! e.g.:
if (ios /= 0) then
print*,'ERROR: could not open file'
stop
end if
Among other things, the program file_access.exe writes the same data to; (i) a text file; and (ii) a binary file:
open(unit=56,file='output.txt',status='replace',iostat=ios,form='formatted')
if (ios /= 0) then
print*,'ERROR: could not open output.txt'
stop
end if
open(unit=57,file='output.bin',status='replace',iostat=ios,form='unformatted')
if (ios /= 0) then
print*,'ERROR: could not open output.bin'
stop
end if
! write size1 and size2 to output files (and then compare sizes)
write(57) array1
write(57) array2
close(57)
write(56,*) array1
write(56,*) array2
close(56)
If you do a long listing('ls -l'), you'll see the size difference:
-rw-r--r-- 1 fred users 220032 Feb 8 11:01 output.bin -rw-r--r-- 1 fred users 825002 Feb 8 11:01 output.txt
Using character strings as file names
cd ../example7
filename.f90 in example7 shows a little trick for people who output a lot of data and need to manipulate a lot of files. It is possible to use a write statement to output a number (or anything else) to a character string and to subsequently use that string as a filename to open, close and output to many files on the fly:
character(len=8) :: filename
integer :: ii, ios
! define a format to write a filename
10 format('output',i2.2)
do ii=1,20
write (unit=filename,fmt=10) ii
open(20,file=filename,status='replace',form='formatted',iostat=ios)
...
Namelists
And all of a sudden, we're at our last example:
cd ../example8
In namelists.f90, we'll look at another approach to file input and output. Fortran provides a way of grouping variables together into a set, called a namelist, that are input or output from our program en masse. This is a common situation. For example, reading in the parameters into a model. The statement:
namelist /my_bundle/ numBooks,initialised,name,vec
sets it up.
Fortran further provides us with built-in mechanisms for reading or writing a namelist to- or from a file.
First, we must open the file of course:
open(unit=56,file='input.nml',status='old',iostat=ios)
if (ios /= 0) then
print*,'ERROR: could not open namelist file'
stop
end if
Note that we made sure to tell Fortran that this is an old file, i.e. that it already exists, and to check the error code. I the case that the open operation failed, we've asked the program to halt with an error.
Now, assuming that we've opened the file OK, we proceed to read its contents. Fortran makes this rather easy for us, given that the information is contained in a namelist:
read(UNIT=56,NML=my_bundle,IOSTAT=ios)
if (ios /= 0) then
print*,'ERROR: could not read example namelist'
stop
else
close(56)
end if
In the read statement, we told fortran that we wanted to read a namelist and that the group of variables should be flagged in the file as my_bundle. Again we've checked the error status and decided to halt with an error should the read statement fail for any reason. Take a look at the contents of input.nml. See that it is ascii text and that the variables (with their values) do not need to be listed in the same order in the file as they are in the program:
&my_bundle numBooks=6 vec=1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 initialised=.false. name='romeo' &end
The program procedes to print the values to screen, demonstrating that they have indeed come from the file, to assign new values to the variables and then to write the modified values to a new file, called modified.nml. Compare the two ascii text files. Try running the program a second time and you will receive an error, telling you that the output could not be written since a file called modified.nml exists and that we expressly stated that is was to be a new file. Delete modified.nml, try again and it will succeed. Try changing the namelist, values, filenames etc. Go for it, make a mess! You'll learn a lot from it:)
Exercises
- Write some code to read in a colour (red, blue, green etc.) from a namelist and then print out the names of all the railway engines (thomas, percy, gordon etc.) that match.
- Read in the dimensions of an ellipse from file and print out it's area.
To go further
The Pragmatic Programming course continues with Linux2, a look at some of the more advanced but very useful Linux concepts.
Now that you are getting familiar with Fortran, go a bit further by reading Fortran2.
We recommend using the most up to date Fortran books, e.g:
Michael Metcalf, John Reid and Malcolm Cohen, Modern Fortran explained, Oxford, 2018, Queens Building Library QA76.73.F25 MET.
Ian Chivers, Jane Sleightholme, Introduction to programming with Fortran, Springer, Fourth edition, 2018, Queens Building Library QA76.73.F25 CHI.
Walter S. Brainerd, Guide to Fortran 2008 programming, Springer, 2015, Queens Building Library QA76.73.F25 BRA.
Richard J. Hanson, Tim Hopkins, Numerical computing with modern Fortran, SIAM, 2013, Queens Building Library, QA76.73.F25 HAN.
Arjen Markus, Modern Fortran in Practice, Cambridge, 2012, Queens Building Library QA76.73.F25 MAR.
Norman S. Clerman, Walter Spector, Modern Fortran: Style and Usage, Cambridge, 2012, Queens Building Library QA76.73.F25 CLE.
Jeanne C Adams et al, The Fortran 2003 handbook, Springer, 2009, Queens Building Library QA76.73.F25 FOR.
Take a look at the 'A Good Read?' page for more details.